Urology
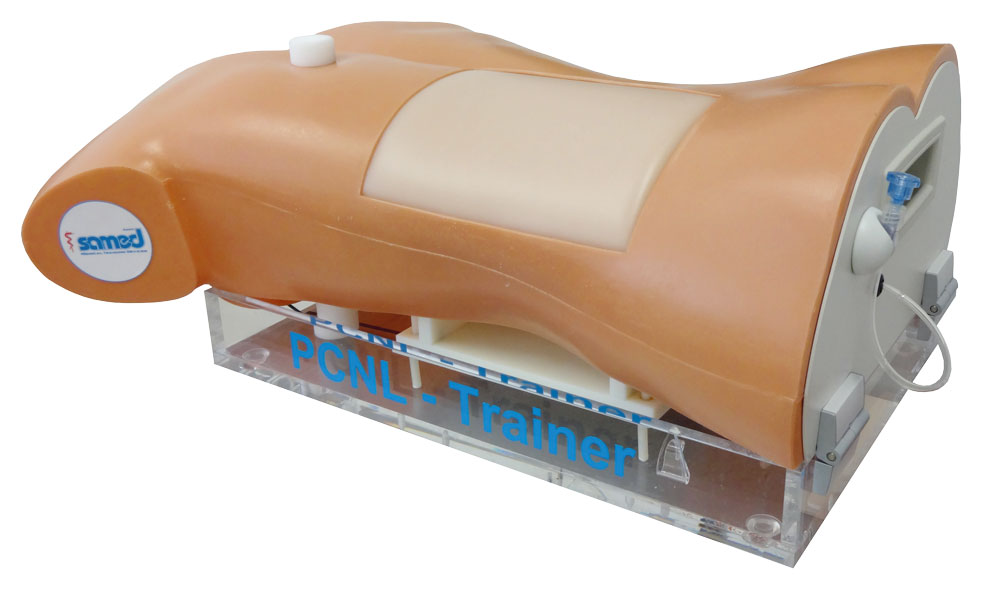
PCNL-Trainer LS40 2.0
This training device has been specially developed for percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy (PCNL) and allows the safe and realistic learning of this therapy method in urology.
The system simulates a prone patient with the appropriate body detail for the procedure. An internal training module (training substrate LSN) with integrated kidney body, the overlying skin layer and a special filling medium in between, make it possible to perform all surgical techniques up to the extraction of kidney stones.
The PCNL trainer offers the unique opportunity to learn and train all required individual steps in a practical way. From location and puncture with or without ultrasound support, via dilation of the puncture channel to the subsequent stone extraction and / or stone fragmentation with their different techniques.
Due to the soft and flexible materials, the puncture of the renal cavity system and the subsequent dilation of the canal are easily possible. Kidney goblets and a renal pelvis are already present in the kidney. External access to the renal pelvis allows insertion of a balloon ureteral catheter.
Depending on the wear, the training module (training substrate LSN) is simply changed after the procedure and thus the operational readiness is restored. The follow-up costs are thus reduced and the downtime is reduced.
SamSon C2 WiFi
With the Samed SamSon C2 WiFi ultrasound scanner and a tablet or Smartphone is it possible to learn the localisation of the kidney and kidney stone. The ultrasound scanner is wireless connected with the tablet or smartphone. The free app can be downloaded for Apple and Android systems. The scan can be wiewed in real time and images can be sved. The SamSon C2 WiFi Ultrasound Scanner is perfect for ultrasound training on our Samed PCNL-Trainer LS40.
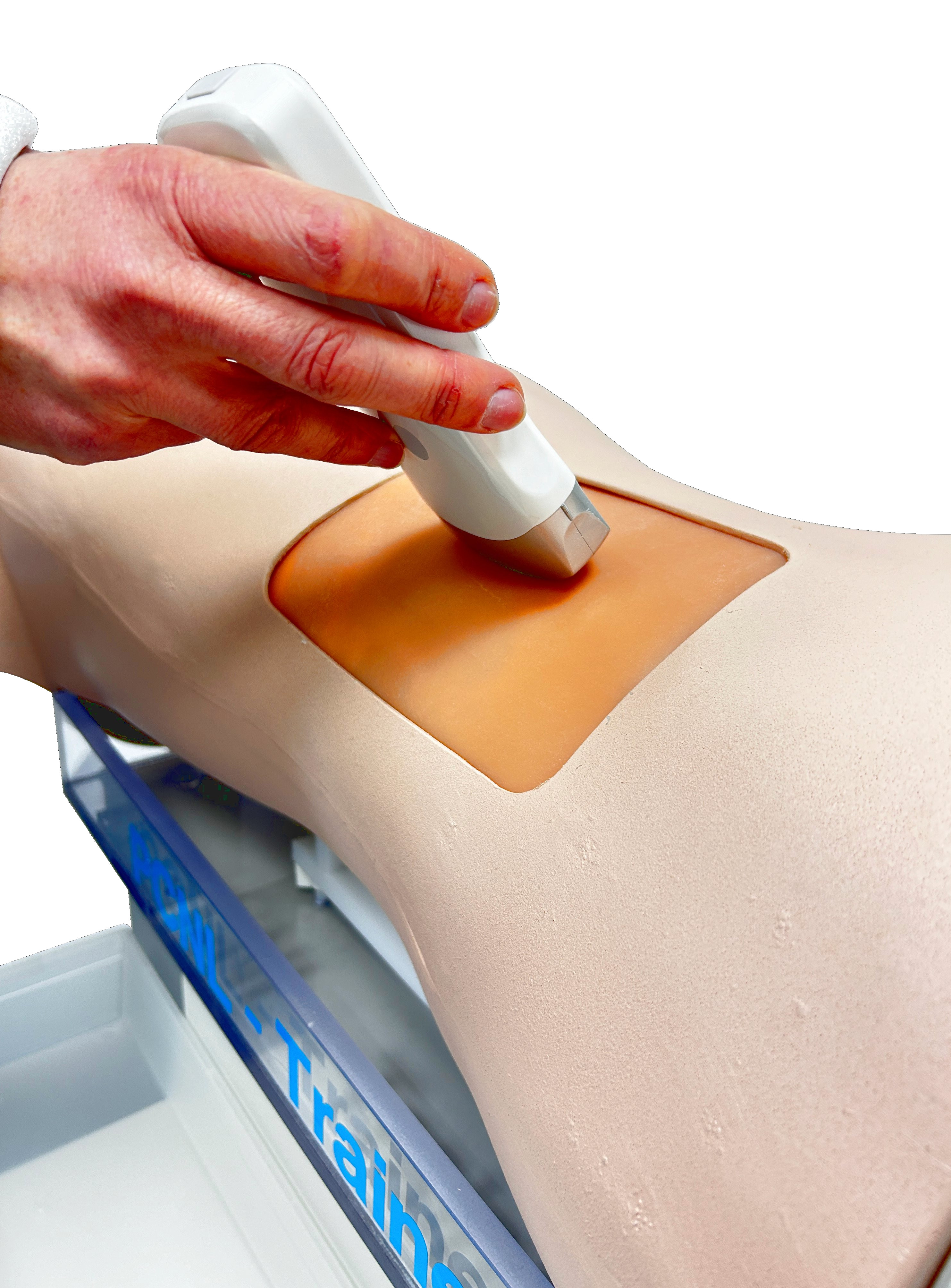
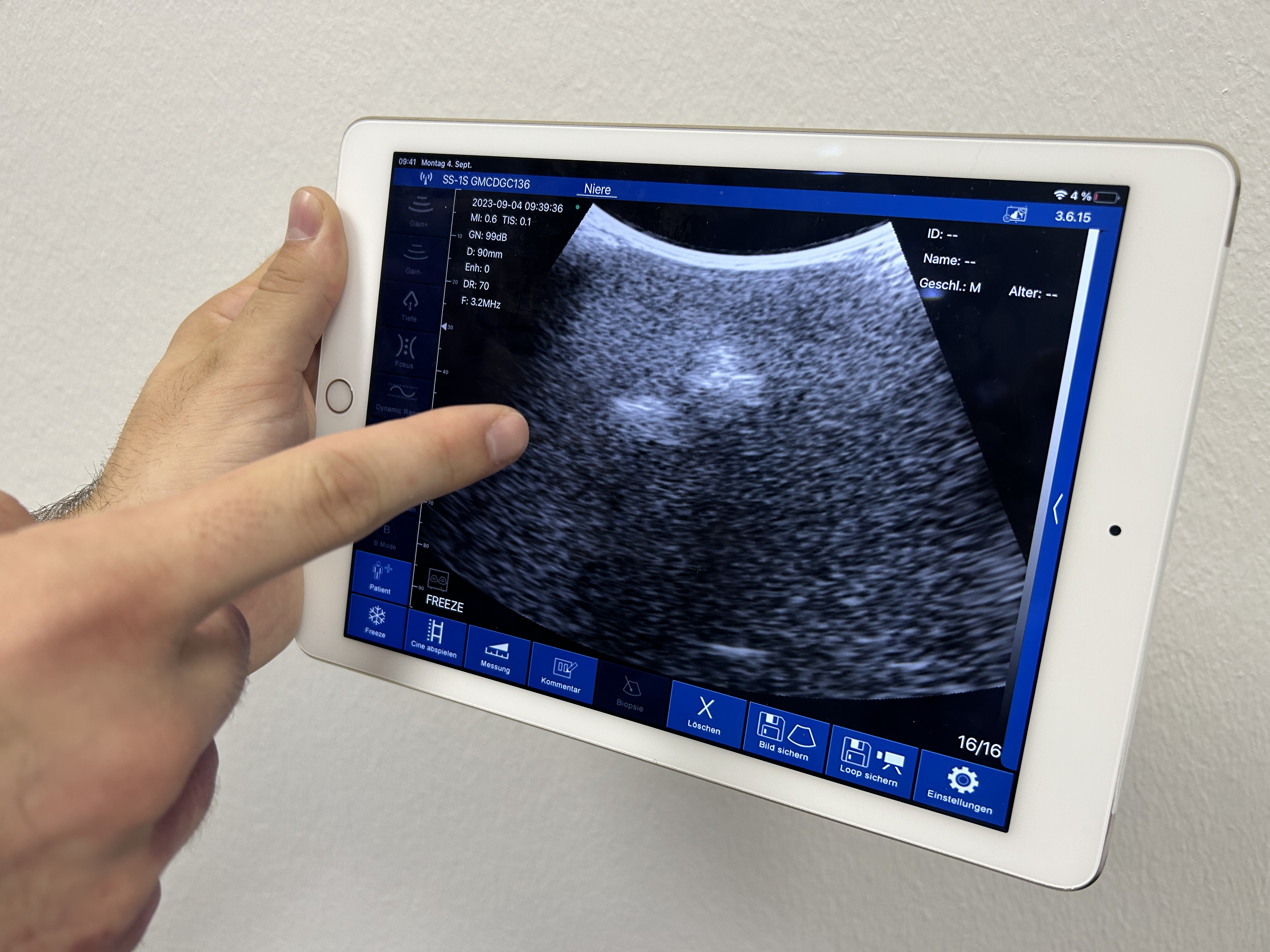
Application example of the PCNL trainer
Presentation of the Samed training device for the realistic tutorial of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. The device offers the unique opportunity to train the puncturing and bougienage of the kidney. The location of the kidney stones is done by means of ultrasound. The subsequent stone extraction forms the conclusion of the training.
Referenzen
Titel:
Percutaneous Nephrostomy Insertion Training: An Overview
Authors:
Ujani Jahvani Reid,Daniel Maruszewski, Matthew Young,
*Chandra Shekhar Biyani, Atif Khan
Titel:
Practical Simulation in urology
Authors:
St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, UKChandra Shekhar Biyani
Catholic University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Ben Van Cleynenbreugel,
Onze Lieve Vrouwziekenhuis Hospital, Aalst, Belgium
Alexandre Mottrie
